Earth Science
Earth Science Helps Students Understand Their World
We are scientists, educators, and your team
Featured Earth Science Lab Books
Featured Earth Science Experiments
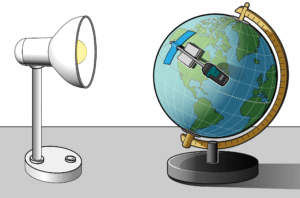
Seasons and Angle of Insolation
In this experiment you will investigate the relationship between angle of insolation and temperature change due to energy absorption from a simulated sun—a light bulb.
Soil pH
When you think of pH, you probably think of liquid acids and bases. But soil can be acidic or basic, too. Soil pH, sometimes referred to as soil acidity, can be expressed using the pH scale. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. Soils with pH above 7 are basic or sweet. Soils with pH below 7 are acidic or sour. A soil with a pH of 7 is neither acidic nor basic, but is neutral.
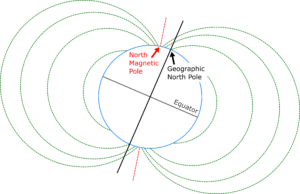
Where IS North?
It depends. Do you mean geographic north or magnetic north? The geographic (true) north pole is the point at 90° N latitude. It is aligned with Earth’s rotational axis. Earth is surrounded by a magnetic field with a north and south magnetic pole. The magnetic north pole is the point to which a compass needle points. It is currently in northern Canada, and is constantly moving due to complex fluid motion in the outer core of Earth. Depending on your location, the difference between magnetic north and geographic north, called magnetic declination, can range from 0° to 30°.
Featured Earth Science Products
-
Go Direct® Temperature Probe
Starts at $78.00 -
Barometer
$79.00 -
Anemometer
$109.00