Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges
Experiment #9 from Human Physiology Experiments: Volume 2
Introduction
The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem, and peripheral nervous system, as well as central and peripheral receptors. These receptors respond to a variety of stimuli including chemicals and pressure. Central respiratory control (respiratory drive) occurs in the pons and medulla oblongata, which respond directly to chemical influences. Other input is received from stretch receptors in the lungs and chemoreceptors located in the carotid and aortic bodies.
At rest, the average adult male produces approximately 200 mL of CO2 each minute, this rate may increase to over 2000 mL/minute with exercise or heavy work. Hyperventilation lowers CO2 levels due to an increased opportunity for gas exchange in the lungs. Holding one’s breath or re-breathing air (such as breathing into a paper bag) raises CO2 levels because there is less opportunity for gas exchange.Chemoreceptors respond most sensitively and rapidly to carbon dioxide, but they also respond to oxygen and pH (acidity). Constant adjustments in the respiratory cycle occur throughout the day to allow gas exchange in the lungs to maintain a steady level of CO2 in the bloodstream. An increase in the CO2 level stimulates breathing, while a decrease inhibits it. If the deviation from the “set point” is large enough, you may experience shortness of breath. The oxygen level can also influence the respiratory cycle, but larger deviations are required before its influence is felt.
In this experiment, you will alter CO2 levels by holding your breath (hypoventilation), rapid breathing (hyperventilation), and exercise. You will compare the respiratory rate, tidal volume, and minute ventilation that result from each physiologic challenge to homeostasis.
Important: The equipment used in this experiment is for educational purposes only and should not be used to diagnose medical conditions.
Objectives
- Obtain graphical representation of normal tidal volume.
- Compare tidal volumes generated by various physiologic challenges.
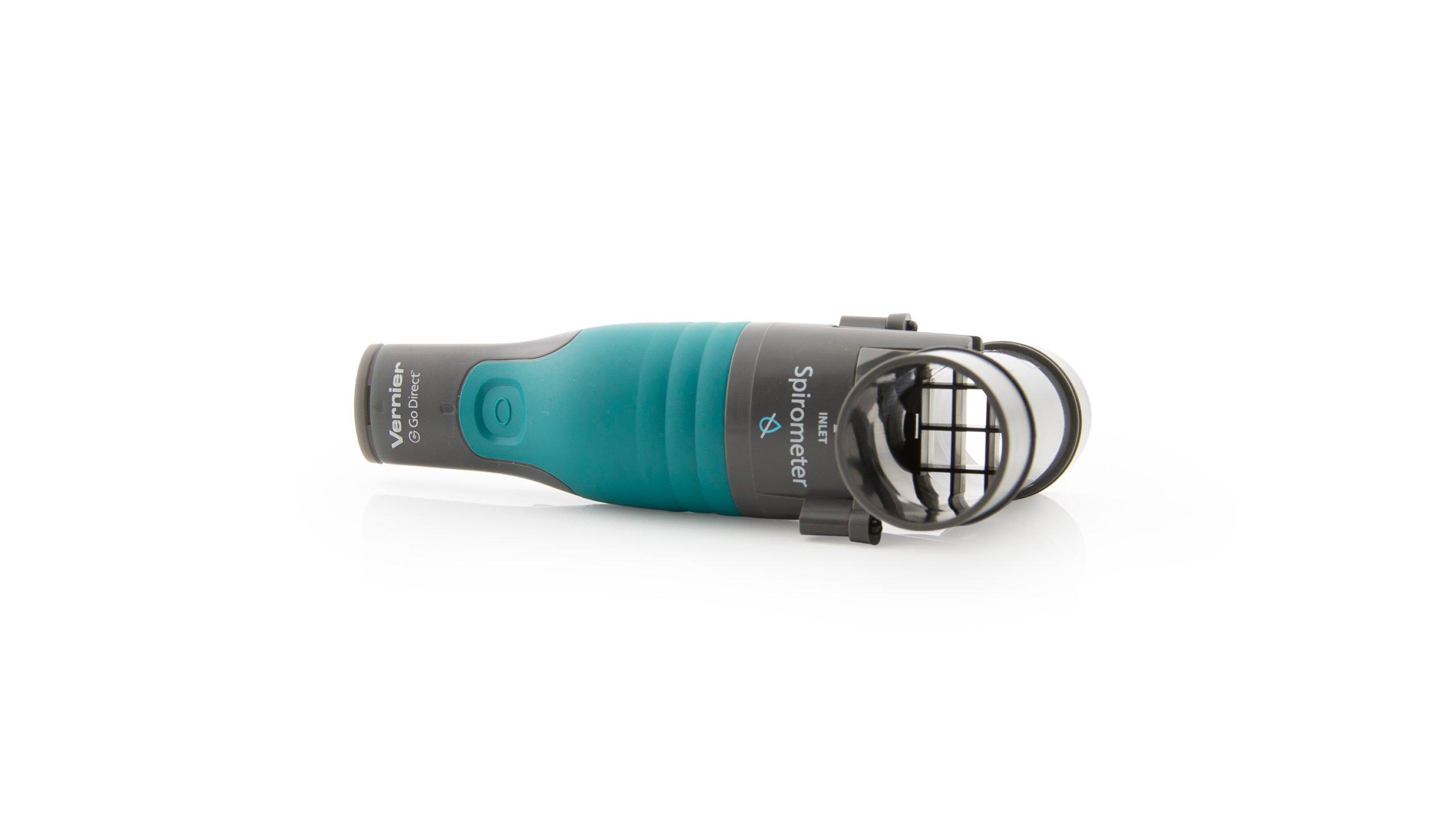
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB)/Sports, Exercise, and Health Science
- 2.1 Structure and function of the ventilatory system
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Biology
- B3.1.5—Ventilation of the lungs
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #9 of Human Physiology Experiments: Volume 2. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.