Introduction
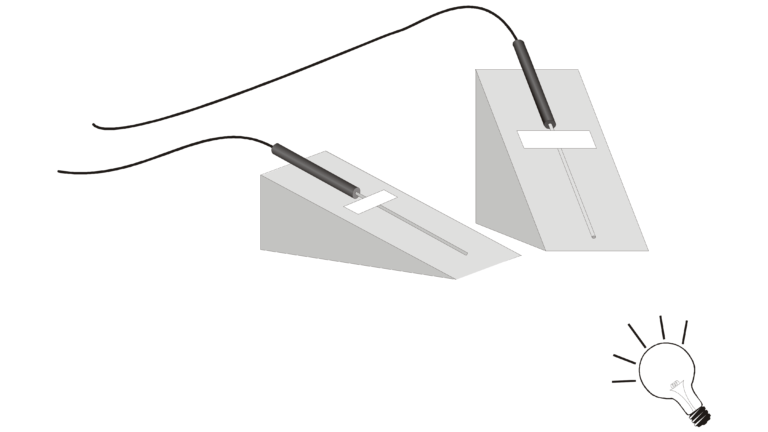
Insolation is the amount of solar radiation received by the Earth or other planet. Because the Earth’s axis is tilted, a location on Earth receives different amounts of solar radiation at different times of the year. In this experiment, a simulated sun—a light bulb—will shine on surfaces positioned at three different angles: 30°, 60°, and 90°. Computer-interfaced Temperature Probes will be used to monitor surface temperature changes caused by radiation from the light bulb.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Measure temperature.
- Graph temperature data.
- Determine the relationship between angle and temperature change.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #14 of Physical Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


