Our new Human Physiology Experiments lab book contains a complete set of laboratory instructions for our Go Direct human physiology sensors. This book also includes several new and exciting activities, such as the “Balance” experiment.
Balance is a complex task that involves input from multiple sensory sources. Visual input, proprioceptors from the limbs and joints, and input from the inner ears are all involved in balance. In “Balance,” students use the accelerometers in the Go Direct® Force and Acceleration Sensor to detect movement while a subject balances on two legs and then on one leg, with eyes open and then closed.
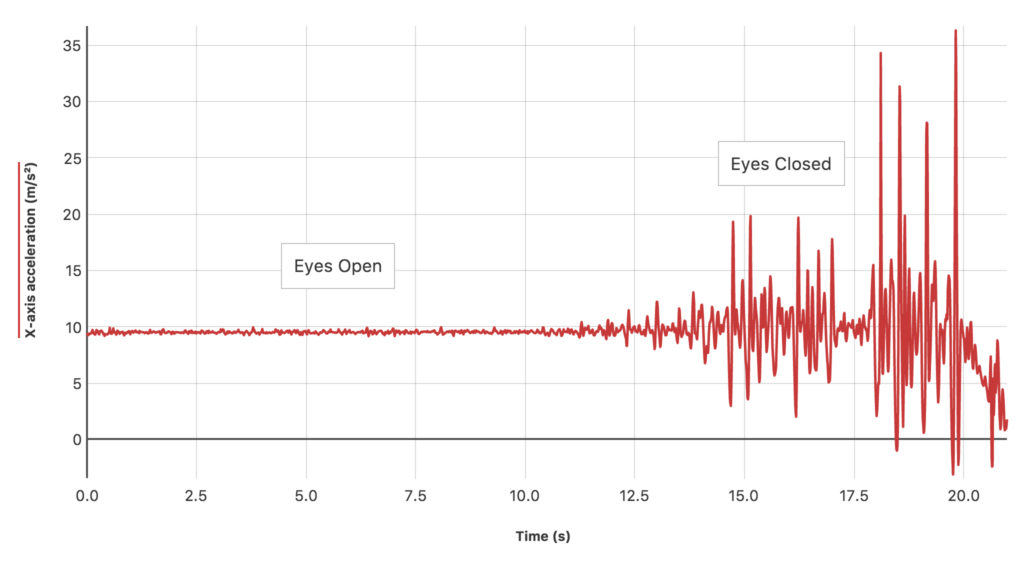
Students intuitively understand that it is much easier to balance with their eyes open, but now they can measure the magnitude of movement for each condition using acceleration data. Less stability results in larger and more frequent movements, which produce greater accelerations. As illustrated by the graph, there is much more movement by the subject when the eyes are closed than when the eyes are open.
This unique and simple activity is an excellent way to explore how different sensory systems are involved in balance.
Download the “Balance” experiment from Human Physiology Experiments.
