
Sharing ideas and inspiration for engagement, inclusion, and excellence in STEM

Happy National Chemistry Week!
This week, we’re standing alongside the science community in recognizing the extraordinary role that chemistry plays in our health and well-being. Countless breakthroughs owe their success to medical experts and scientists who have drawn inspiration from the healing properties of plants and animals, age-old practices of ancient peoples, and our own bodies’ innate mechanisms to prevent and fight disease as well as heal and restore us to health.
Join us in celebrating National Chemistry Week with four experiments from Vernier that explore the profound connections between chemistry and human health.
1. The Synthesis and Analysis of Aspirin
Experiment #22 from Advanced Chemistry with Vernier
Aspirin, the ubiquitous pain reliever, is chemically referred to as acetylsalicylic acid. One of the compounds used in the synthesis of aspirin is salicylic acid, which is itself a pain reliever that was known to many cultures, including many Native American tribes who extracted it from willow tree bark.
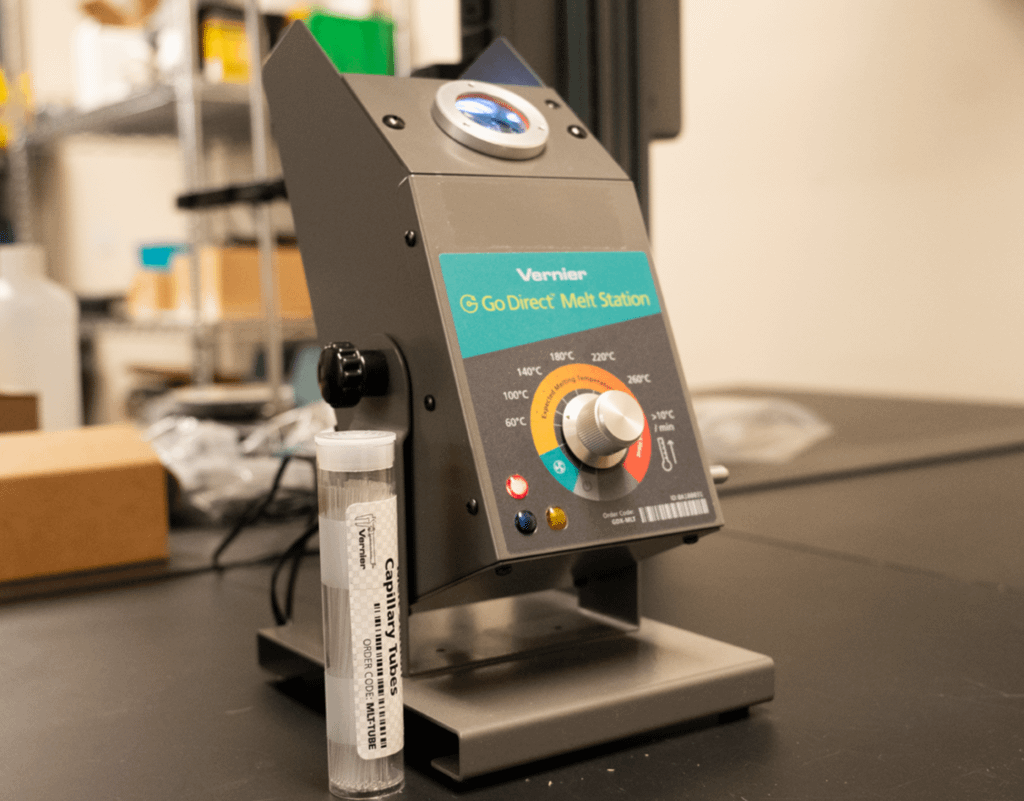

In this experiment, students will synthesize and analyze aspirin by reacting acetic anhydride with salicylic acid in the presence of phosphoric acid (which acts as a catalyst).
This experiment includes the following objectives:
- Synthesize a sample of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin).
- Calculate the percent yield of your synthesis.
- Measure the melting temperature of your aspirin sample.
- Conduct a colorimetric analysis of your aspirin sample.
2. Time-Release Vitamin C Tablets
Experiment #31 from Chemistry with Vernier
By slowly releasing a vitamin or a medicine throughout the day, timed-release tablets offer a simple alternative to multiple doses. There are several different methods used to achieve the timed-release effect. One common method involves covering the medicine with a polymer coating that allows it to slowly permeate into the body.
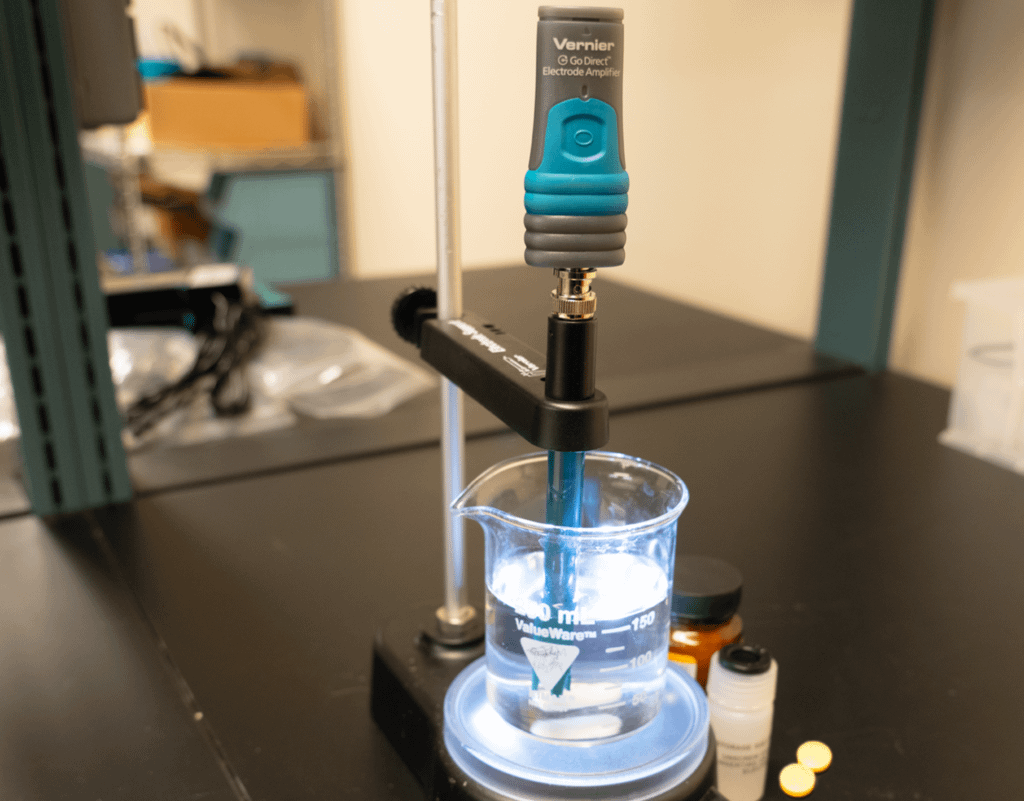

In this experiment, students will investigate and compare the differences between regular and time-release vitamin C tablets.
This experiment includes the following objectives:
- Compare the behavior of timed-release vitamin C tablets with regular vitamin C tablets when each is added to distilled water.
- Use a pH Sensor to monitor the pH value of the two different types of vitamin C tablets over an elapsed time of approximately twelve minutes.
3. Determining the Quantity of Iron in a Vitamin Tablet
Experiment #34 from Chemistry with Vernier
As biochemical research advances, our understanding of the significance of metallic elements in the human body grows. For example, copper and zinc are present in enzymes, and trace amounts of molybdenum and selenium are vital in regulating internal oxidation-reduction reactions. Iron is another important metal, which is necessary for oxygen transport in the bloodstream. Many people gain these essential elements through their diets or by taking multivitamin tablets.
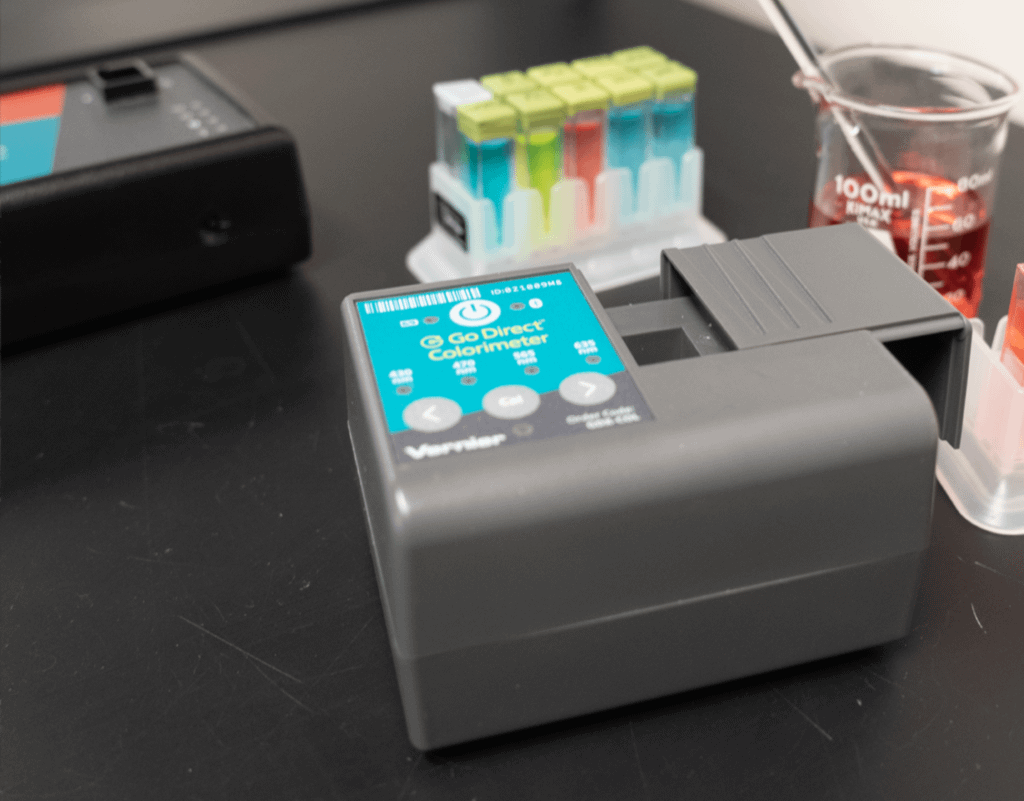

In this experiment, students will use a Colorimeter or Spectrometer to measure the absorbance of a solution prepared from a multivitamin tablet. This absorbance value is converted to concentration using the Beer’s law curve. From this concentration, the total mass of iron in the original tablet can be calculated.
This experiment includes the following objectives:
- Prepare Fe2+ standard solutions.
- Measure the absorbance of each standard solution.
- Plot a graph of absorbance of Fe2+ vs. concentration.
- Use a sensor and your Beer’s law plot to determine the quantity of iron in a vitamin tablet.
4. Electrolytes in Energy Drinks
Experiment #06 from Food Chemistry Experiments
We all need electrolytes in our diet. Why? Electrolytes are used by our nerves and muscles. Among other things, they regulate our blood pressure and pH of our blood and help keep our tissues hydrated. As the name implies, in many cases, electrolytes are involved with carrying electrical current in our bodies. During exertion we can lose electrolytes through sweating, which is why athletes commonly drink beverages high in electrolytes.
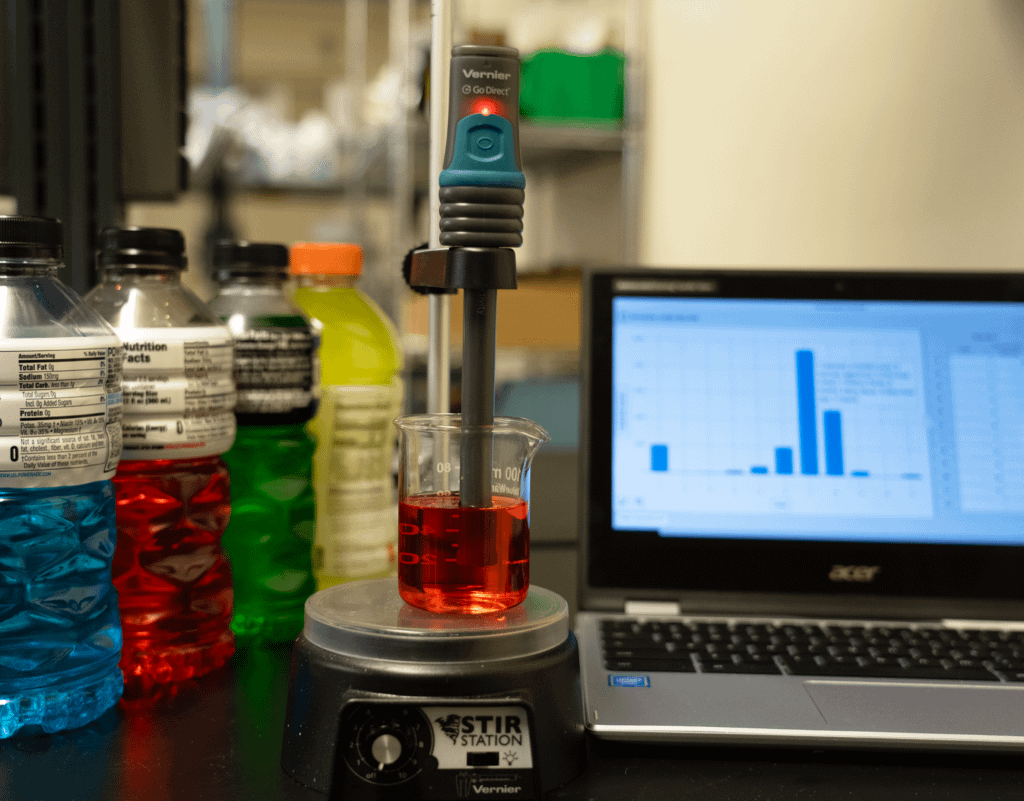
In this experiment, students will analyze the components of a popular sports drink used by athletes to replenish electrolytes and water lost during physical activity.
This experiment includes the following objectives:
- Write equations for the dissociation of compounds in water.
- Use a conductivity probe to measure the conductivity of solutions.
- Determine which molecules or ions are responsible for the conductivity of solutions.
Let us know how you’re celebrating National Chemistry Week!
Want to know more about these experiments or sensors? We’re always here to help! Reach out to our Tech Support team at chemistry@vernier.com or call 888-837-6437.
Share this Article

Sign up for our newsletter
Stay in the loop! Beyond Measure delivers monthly updates on the latest news, ideas, and STEM resources from Vernier.






