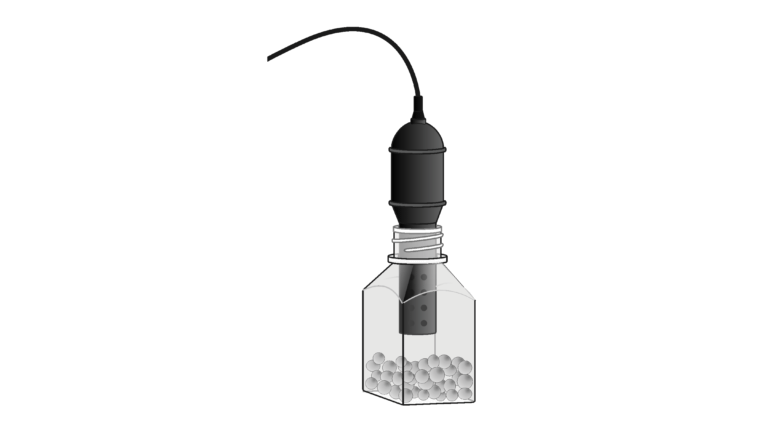
Introduction
Cell respiration refers to the process of converting the chemical energy of organic molecules into a form immediately usable by organisms. Glucose may be oxidized completely if sufficient oxygen is available according to the following equation:
All organisms, including plants and animals, oxidize glucose for energy. Often, this energy is used to convert ADP and phosphate into ATP. Peas undergo cell respiration during germination. Do peas undergo cell respiration before germination? Using your collected data, you will be able to answer the question regarding respiration and non-germinating peas.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Measure gas production.
- Study the effect of temperature on cell respiration.
- Determine whether germinating peas and non-germinating peas respire.
- Compare the rates of cell respiration in germinating and non-germinating peas.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1

Option 2

Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #5B of Advanced Biology with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.

