Introduction
Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships in chemical reactions. A balanced chemical reaction equation gives the mole ratios of the reactants and the products as coefficients. When some of the chemical formulas are not known, an experiment can be conducted to help determine the mole ratios.
Acetic acid (HC2H3O2) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are the reactants in the acid-base reaction to be investigated in the Preliminary Activity. Sodium hydroxide neutralizes acetic acid according to the unbalanced and incomplete equation:
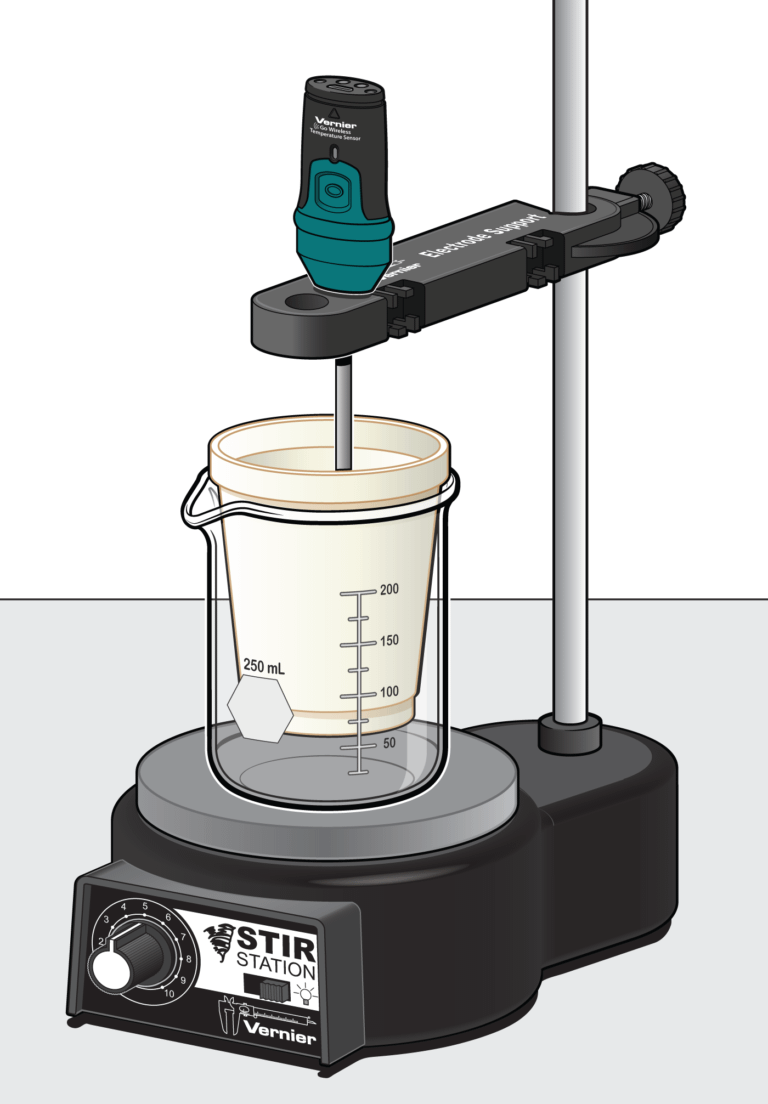
It is possible to identify the coefficients of the reactants without knowing the products of the reaction. The process that you will use to determine the coefficients is called continuous variations. You will prepare a series of mixtures of the two reactants. Each mixture will have the same total volume and the same total number of moles of reactants. The reaction is exothermic, thus the mixture that generates the most heat energy will be the reaction that completely consumes both the reactants. You will use this mixture to establish the coefficients, and therefore the mole ratio of the reactants, for the reaction.
Objectives
In the Preliminary Activity, you will gain experience using a Temperature Probe, data-collection software, and the continuous variations method as you determine the sodium hydroxide to acetic acid mole ratio in the chemical equation for the reaction between sodium hydroxide and acetic acid.
After completing the Preliminary Activity, you will first use reference sources to find out more about acid-base reactions, balanced equations, and mole ratios before you choose and investigate a researchable question that utilizes the continuous variations method to determine the mole ratio of reactants in an acid-base reaction.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #10 of Investigating Chemistry through Inquiry. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


