Sugar Fermentation by Yeast
Experiment #24 from Investigating Chemistry through Inquiry
- Subject
- Chemistry
Introduction
Yeast can metabolize sugar in two ways, aerobically, with the aid of oxygen, or anaerobically, without oxygen. When yeast metabolizes a sugar under anaerobic conditions, ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas are produced. An equation for the fermentation of the simple sugar glucose (C6H12O6) is:
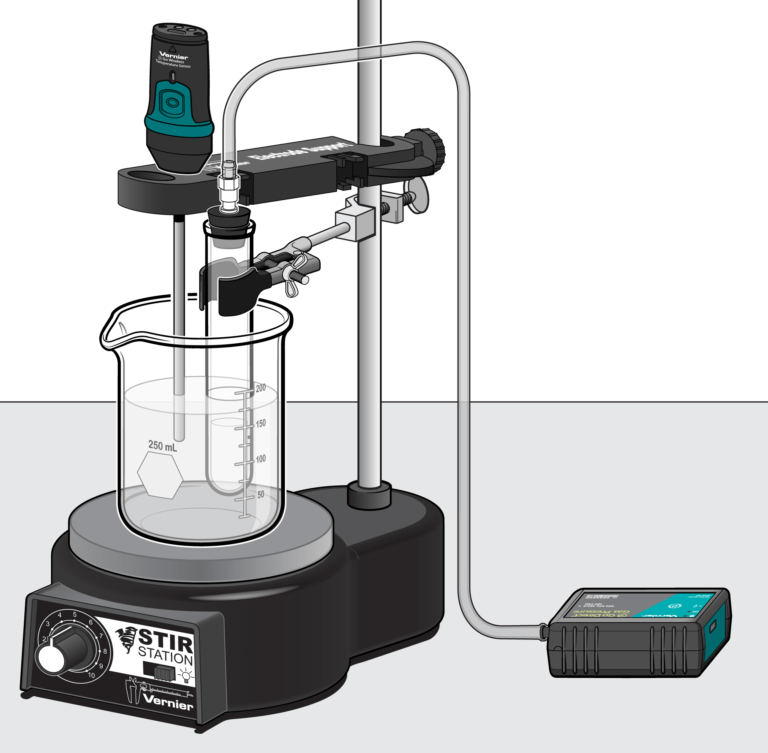
The metabolic activity of yeast can be determined by the measurement of gas pressure inside the fermentation vessel.
Objectives
In the Preliminary Activity, you will use a Gas Pressure Sensor to monitor the pressure inside a test tube as yeast metabolizes glucose anaerobically. When data collection is complete, you will perform a linear fit on the resultant graph to determine the fermentation rate.
After completing the Preliminary Activity, you will first use reference sources to find out more about sugar fermentation by yeast before you choose and investigate a researchable question dealing with fermentation.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #24 of Investigating Chemistry through Inquiry. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.