Additivity of Heats of Reaction: Hess’s Law
Experiment #18 from Chemistry with Vernier
- Education Level
- High School
- Subject
- Chemistry
Introduction
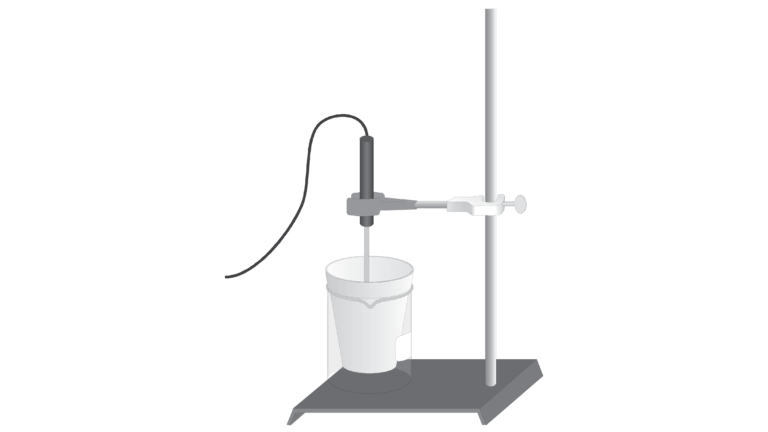
In this experiment, you will use a Styrofoam-cup calorimeter to measure the heat released by three reactions. One of the reactions is the same as the combination of the other two reactions. Therefore, according to Hess’s law, the heat of reaction of the one reaction should be equal to the sum of the heats of reaction for the other two. This concept is sometimes referred to as the additivity of heats of reaction. The primary objective of this experiment is to confirm this law.
The reactions we will use in this experiment are:
(1) Solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in water to form an aqueous solution of ions.
(2) Solid sodium hydroxide reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid to form water and an aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
(3) Solutions of aqueous sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react to form water and aqueous sodium chloride.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Combine equations for two reactions to obtain the equation for a third reaction.
- Use a calorimeter to measure the temperature change in each of three reactions.
- Calculate the heat of reaction, ΔH, for the three reactions.
- Use the results to confirm Hess’s law.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1
Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Chemistry
- Reactivity 1.2.4—An application of Hess’s law uses enthalpy of formation data or enthalpy of combustion data to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #18 of Chemistry with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


