Photovoltaic Cells
Experiment #29 from Investigating Environmental Science through Inquiry
- Subject
- Environmental Science
Introduction
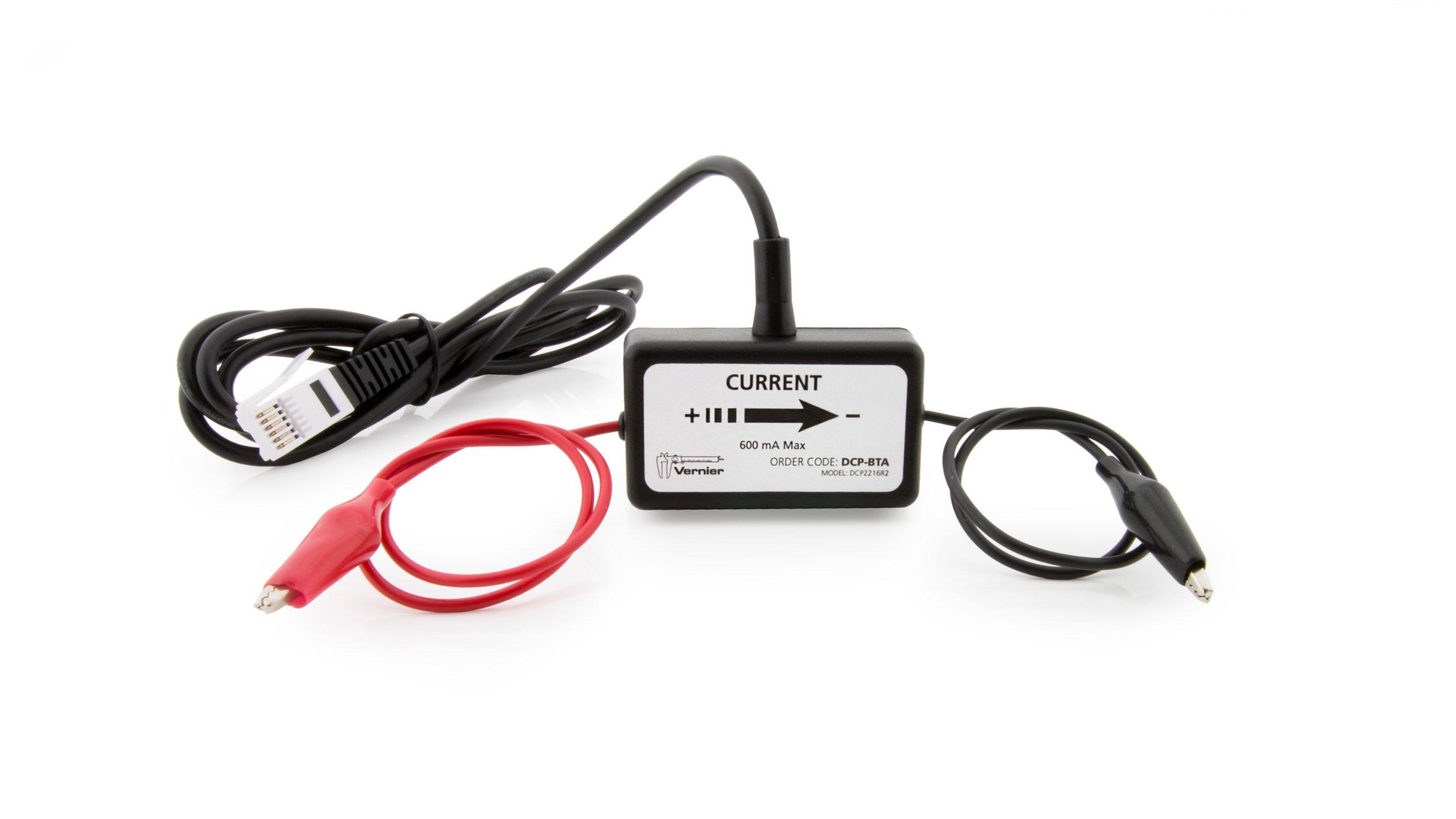
Energy produced by the sun is called solar energy. It is produced during nuclear reactions that take place throughout the volume of the sun. The energy travels to Earth in the form of light. Photovoltaic (PV) cells, or solar cells, change the light energy to electrical energy that can be used to power calculators, cars or even satellites. A photovoltaic cell is usually made of a semiconducting material such as silicon. When light strikes the cell, it provides enough energy to move electrons through the cell producing an electric current. A single photovoltaic cell is approximately the size of a fingernail and puts out a very small current when struck by the light. Objects requiring higher currents to operate can be powered by wiring large numbers of photovoltaic cells together.
Items powered by solar energy are said to be using solar power. Streetlights that must operate in the dark store the energy in a battery while the sun is shining and then use the energy at night. Scientists working in remote places rely on solar power to operate their computers and equipment. What things can you think of that are powered by solar energy?
Objectives
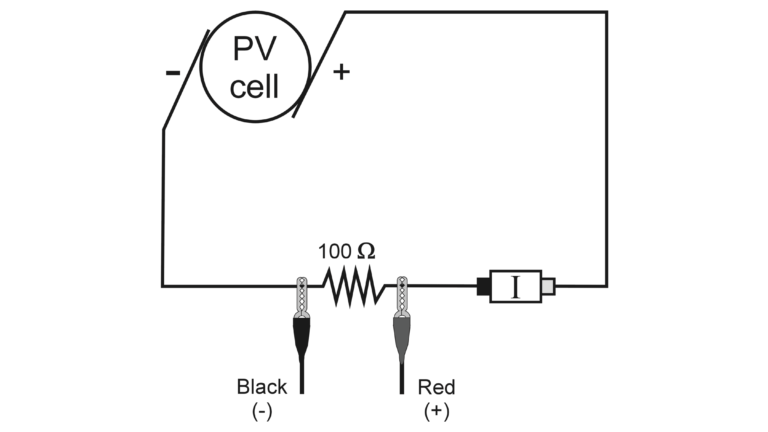
In the Preliminary Activity, you will measure the current and voltage produced by a photovoltaic cell when exposed to sunlight. You will calculate the power output of the cell using the relationship
Where power has units of watts (W), voltage has units of volts (V), and current has units of amperes (A).
After completing the Preliminary Activity, you will first use reference sources to find out more about photovoltaic cells before you then choose and investigate a researchable question.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #29 of Investigating Environmental Science through Inquiry. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.



