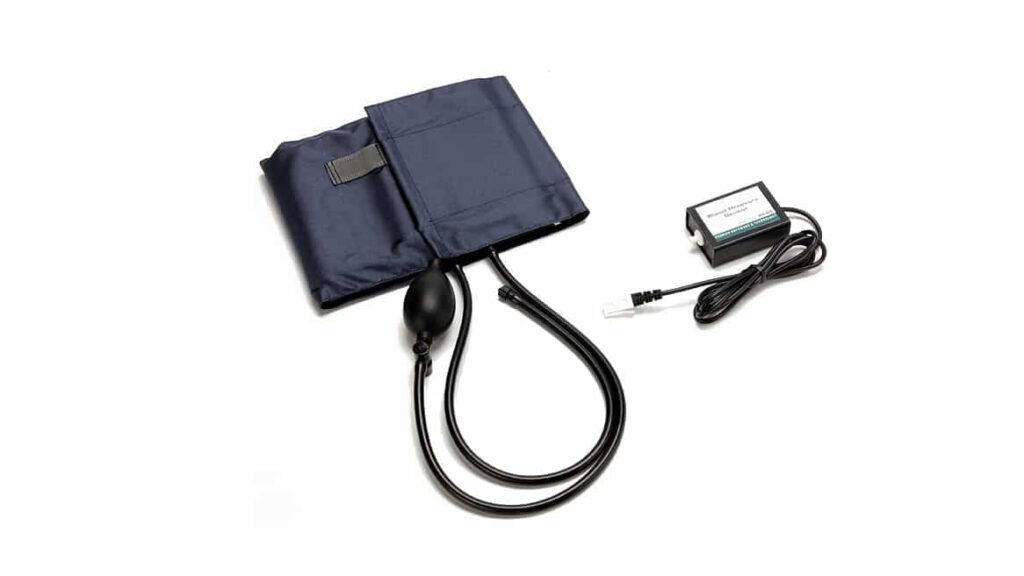
Blood Pressure Sensor User Manual
Order Code: BPS-BTA
The Vernier Blood Pressure Sensor is used to measure systemic arterial blood pressure in humans (non-invasively). When used with the appropriate software, it can measure mean arterial blood pressure and calculate both the systolic and diastolic blood pressure using the oscillometric method.
Note: Vernier products are designed for educational use. Our products are not designed nor are they recommended for any industrial, medical, or commercial process such as life support, patient diagnosis, control of a manufacturing process, or industrial testing of any kind.
What's Included
- Blood Pressure Sensor
- Standard adult size adjustable cuff (27 cm to 39 cm)
- Bulb pump (with release valve)
Compatible Software and Interfaces
Choose a platform below to see its compatibility requirements.LabQuest
Interface LabQuest App LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support LabQuest Full support Computers
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis (Web App) Logger Pro (discontinued) Logger Lite (discontinued) LabQuest Mini Full support Full support Full support Full support LabQuest 3 Full support Full support Full support Incompatible LabQuest 2 Full support Full support Full support Full support LabQuest Stream Full support 1 Full support 1 Partial support 2 Full support 1 Go!Link Full support Full support Full support Full support LabQuest Full support Full support Full support Full support LabPro Incompatible Incompatible Full support Full support Compatibility Notes
Chromebook
Software Interface Graphical Analysis (Web App) LabQuest Mini Full support LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support LabQuest Stream Full support 1 Go!Link Full support LabQuest Full support Compatibility Notes
iOS
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis GW LabQuest Stream Full support Incompatible LabQuest 3 Full support 1 Full support 1 LabQuest 2 Full support 1 Full support 1 Compatibility Notes
Android
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis GW LabQuest Stream Full support Incompatible LabQuest 3 Full support 1 Full support 1 LabQuest 2 Full support 1 Full support 1 Compatibility Notes
Arduino
Software Interface Arduino Vernier Arduino® Interface Shield Full support 1 Compatibility Notes
LabVIEW
Software Interface NI LabVIEW SensorDAQ Full support 1 Vernier myDAQ Adapter Full support 1 2 Go!Link Full support 1 LabQuest Mini Full support LabQuest Stream Full support LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support LabQuest Full support Compatibility Notes
Quick Start
- Plug the sensor into the interface (LabQuest 3, LabQuest Mini, etc.).
- Connect the interface to your device.
- If using USB, connect to the USB port on your computer.
- If using Bluetooth® wireless technology, click your interface type and then select your device.
- Prepare for data collection:
- Vernier Graphical Analysis®: Launch the app, if necessary, and click Sensor Data Collection.
- LabQuest® App: Choose New from the File menu.
The software will identify the sensor and load a default data-collection setup. You are now ready to collect data.
Need Additional Information?
Visit the following link:
www.vernier.com/start-lq-sensor
Note: Vernier products are for educational use only.
Using the Product
Connect the sensor following the steps in the Quick Start section of this user manual.
When performing blood pressure measurements, it is best to work with a partner. Follow these general procedures when using the Blood Pressure Sensor:
- Connect the Blood Pressure Sensor to the interface. Attach the rubber hose from the cuff to the connector on the sensor.
- Wrap the cuff firmly around your partner’s arm, approximately 2 cm above the elbow. The two rubber hoses from the cuff should be positioned over the bicep muscle (brachial artery) and not under the arm. Important: The person having his or her blood pressure measured must remain still during data collection—no movement of the arm or hand during measurements.
- Begin data collection.
- Quickly and repeatedly squeeze the bulb to inflate the cuff on your partner’s arm. Continue inflating the cuff to a pressure between 150 and 170 mm Hg. A meter in the data-collection software will display the live pressure readings from the sensor. When the maximum pressure is reached, set the bulb pump down onto the table. The built-in pressure release valve will slowly deflate the cuff.
- After the pressure drops to 50 mm Hg, you may press down on the pressure release valve to release any air left in the cuff. If the pressure does not reach 50 mm Hg by the time data collection ends, adjust the exhaust rate of the pressure release valve according to the directions listed under “Adjusting the Pressure Release Valve.”
Specifications
|
Response time |
1 ms |
|
Pressure range |
0 mm Hg to 258 mm Hg |
|
Maximum pressure without permanent damage |
1550 mm Hg |
|
Typical accuracy |
± 1 mm Hg |
|
Combined linearity and hysteresis |
typical ±0.25% |
|
Temperature compensated |
–20°C to 85°C |
|
Default calibration values |
|
How the Sensor Works
The sensor produces an output voltage that varies with the pressure measured in the cuff. It includes special circuitry to minimize errors caused by changes in temperature. We also provide a filtering circuit that conditions the signal from the pressure transducer. The output voltage from the Blood Pressure Sensor is linear with respect to pressure. The software used with the sensor calculates the blood pressure parameters.
Calculating Blood Pressure (Oscillometric Method)
The software used with the sensor determines the blood pressure of the subject by using the oscillometric method, a non-invasive means of measuring blood pressure. It is based on the principle that blood pumped through the arteries by the heart causes the arterial walls to flex. When a cuff (placed around the upper arm to occlude the brachial artery) is inflated and then slowly deflated at a constant rate, an arterial pressure pulse forms. These pressure pulses pass from the arteries, through the arm, and into the pressure cuff itself.
When the artery is fully compressed, blood flow stops along with the pulsations. As the pressure in the cuff is slowly decreased, the arterial blood pressure increases to the point that blood is forced through the artery in short pulses. As the pressure in the cuff continues to decrease, more blood flows through the occluded artery and the pulses become increasingly significant until maximum amplitude is reached. Further decrease of the cuff pressure minimizes the occlusion of the artery and the pulses continue to decrease until the occlusion is removed.
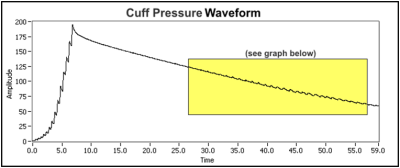
Cuff pressure measured by sensor
These pressure pulses, when separated from the decaying mean pressure of the cuff, form an oscillating waveform. The peak-to-peak amplitudes of this waveform create a bell shaped “envelope”. Within the envelope, the amplitudes of the waveform increase through the systolic blood pressure and continue increasing until the mean arterial pressure (MAP) is reached. Physiologically, the cuff pressure corresponding to the maximum amplitude approximates the mean arterial pressure. Generally, the systolic blood pressure is calculated by determining the point along the envelope prior to the MAP using a known percentage of the maximum amplitude. Diastolic blood pressure is calculated using the same method and the portion of the envelope following the MAP.
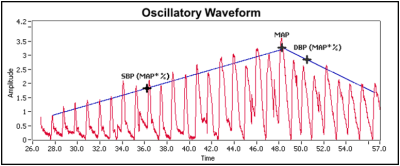
Oscillatory waveform used to create “envelope”
Troubleshooting
Note that the Blood Pressure Sensor will not report blood pressure parameters until data collection has ended. Also note that you need to let the data-collection software finish collecting data to get accurate blood pressure readings. Do not stop data collection prematurely, allow the software to complete data collection.
Blood pressure readings will differ from person to person and even between measurements on the same individual. Do not expect to receive the same measurements on each trial since there are many factors that cause a person’s blood pressure to increase or decrease. Use the following tips to take accurate measurements.
Helpful Tips
- The subject’s arm and hand must remain still during measurements.
- Proper placement of the pressure cuff will increase the accuracy of your blood pressure measurements. The rubber hoses from the cuff should exit over the brachial artery and 2 cm above the crease in the elbow.
- Accurate blood pressure readings depend on the use of a cuff of appropriate size for the arm. For younger students, a smaller cuff is available (18 cm to 27 cm). Our small blood pressure cuff can be ordered separately (order code CUFF-SM). A large cuff is also available for students with arm circumferences greater than 39 cm (order code CUFF-LG).
- Do not to touch or move the exhaust valve during measurements.
- Remove any clothing that may cover or constrict the portion of the arm being measured.
- For most individuals it is not necessary to inflate the pressure cuff higher than 170 mm Hg. Over inflation of the cuff may cause pain and/or injury.
- If the pressure release valve is exhausting slower or faster than 2.0 to 4.0 mm Hg/s, then adjust the exhaust rate of the pressure valve.
For more information see www.vernier.com/til/1426
Adjusting the Pressure Release Valve
The pressure release valve is set to release at a rate of 3.0 mm Hg/s on an arm that is 32 cm in circumference. For arms much larger or much smaller it may be necessary to adjust the valve so that the exhaust rate stays in the range of 2.0 to 4.0 mm Hg/s. With the bulb in hand and the hose leading away from you, place a screwdriver into the metal slot on the top of the release valve. To increase the rate of exhaust, turn the screwdriver clockwise. To decrease the rate of exhaust, turn the screwdriver counter-clockwise. The larger a subject’s arm the slower the release valve will exhaust.
Using the BPS at High Altitudes (above 6,000 ft)
To record proper measurements at altitudes above 6,000 ft (0.8 atm or 609 mm Hg) the pressure release valve will need to be readjusted. The pressure release valve is set to release at a rate of 3.0 mm Hg/s at sea level, where atmospheric pressure is 1 atm or 760 mm Hg. At higher altitudes, the pressure release valve will exhaust at a slower rate. To use the Blood Pressure Sensor at altitudes above 6,000 ft, open the pressure exhaust valve by turning it a half turn clockwise. See the instructions above. Verify that the exhaust rate is now in the range of 2.0–4.0 mm Hg/s after making the adjustment.
Repair Information
If you have watched the related product video(s), followed the troubleshooting steps, and are still having trouble with your Blood Pressure Sensor, contact Vernier Technical Support at support@vernier.com or call 888-837-6437. Support specialists will work with you to determine if the unit needs to be sent in for repair. At that time, a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number will be issued and instructions will be communicated on how to return the unit for repair.
Accessories/Replacements
| Item | Order Code |
|---|---|
|
CUFF-STD |
|
|
CUFF-LG |
|
|
CUFF-SM |
Warranty
Warranty information for this product can be found on the Support tab at www.vernier.com/bps-bta/#support
General warranty information can be found at www.vernier.com/warranty
Contact Support
Fill out our online support form or call us toll-free at 1-888-837-6437.