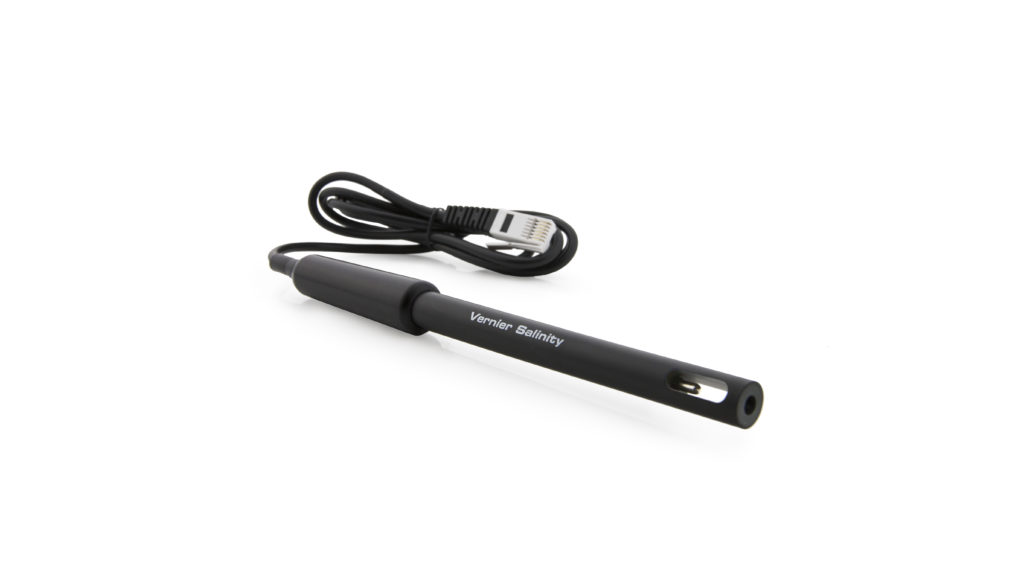
Salinity Sensor User Manual
Order Code: SAL-BTA
The Salinity Sensor measures the conductivity of a solution with a high ion concentration. Salinity is the total of all non-carbonate salts dissolved in water, usually expressed in parts per thousand (1 ppt = 1000 mg/L). Salinity is an important measurement in seawater. The salinity level in seawater is fairly constant, at about 35 ppt (35,000 mg/L).
- Use this sensor for an accurate on-site measurement of salinity in ocean water.
- With this sensor, students can qualitatively see the difference between the ionic and molecular nature of substances in aqueous solution.
- Use the sensor to confirm the direct relationship between salinity and ion concentration in an aqueous solution. Concentrations of unknown samples can then be determined.
- Monitor the rate of reaction in a chemical reaction in which dissolved ions and solution salinity varies with time due to an ionic species being consumed or produced.
Note: Vernier products are designed for educational use. Our products are not designed nor are they recommended for any industrial, medical, or commercial process such as life support, patient diagnosis, control of a manufacturing process, or industrial testing of any kind.
Compatible Software
Choose a platform below to see its compatibility requirements.LabQuest
Interface LabQuest App LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support LabQuest Full support Computers
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis (Web App) Logger Pro (discontinued) Logger Lite (discontinued) LabQuest Mini Full support Full support Full support Full support LabQuest 3 Full support Full support Full support Incompatible LabQuest 2 Full support Full support Full support Full support LabQuest Stream Full support 1 Full support 1 Partial support 2 Full support 1 Go!Link Full support Full support Full support Full support LabQuest Full support Full support Full support Full support LabPro Incompatible Incompatible Full support Full support Compatibility Notes
Chromebook
Software Interface Graphical Analysis (Web App) LabQuest Mini Full support LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support LabQuest Stream Full support 1 Go!Link Full support LabQuest Full support Compatibility Notes
iOS
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis GW LabQuest Stream Full support Full support LabQuest 3 Full support 1 Full support 1 LabQuest 2 Full support 1 Full support 1 Compatibility Notes
Android
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis GW LabQuest Stream Full support Partial support 1 LabQuest 3 Full support 2 Full support 2 LabQuest 2 Full support 2 Full support 2 Compatibility Notes
Arduino
Software Interface Arduino Vernier Arduino® Interface Shield Full support LabVIEW
Software Interface NI LabVIEW SensorDAQ Full support Vernier myDAQ Adapter Full support 1 Go!Link Full support LabQuest Mini Full support LabQuest Stream Full support LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support LabQuest Full support Compatibility Notes
Texas Instruments
Software Interface EasyData DataMate TI-84 SmartView DataQuest TI-Nspire Software EasyLink Full support 1 Incompatible Full support 2 Full support Full support 2 CBL 2 Full support 3 Full support 3 4 Incompatible Incompatible Incompatible LabPro Full support 3 Full support 3 4 Incompatible Incompatible Incompatible TI-Nspire Lab Cradle Incompatible Incompatible Incompatible Full support Full support Compatibility Notes
Quick Start
- Plug the sensor into the interface (LabQuest 3, LabQuest Mini, etc.).
- Connect the interface to your device.
- If using USB, connect to the USB port on your computer.
- If using Bluetooth® wireless technology, click your interface type and then select your device.
- Prepare for data collection:
- Vernier Graphical Analysis®: Launch the app, if necessary, and click Sensor Data Collection.
- LabQuest® App: Choose New from the File menu.
The software will identify the sensor and load a default data-collection setup. You are now ready to collect data.
Need Additional Information?
Visit the following link:
Using the Product
Taking Measurements with the Salinity Sensor
- Rinse the tip of the Salinity Sensor with distilled water. Blot the inside of the electrode cell dry to avoid water droplets diluting or contaminating the sample to be tested.
- Insert the tip of the sensor into the sample to be tested. Important: Be sure the electrode surfaces in the elongated cell are completely submerged in the liquid and that there are no bubbles around the electrode surface.
- While gently swirling the probe, wait for the reading on your data-collection device to stabilize. This should take about 10 seconds.
- Important: Do not completely submerge the sensor. The handle is not waterproof.
- Rinse the end of the probe with distilled water before taking another measurement.
- If you are taking readings at temperatures below 15°C or above 30°C, allow more time for the temperature compensation to adjust and provide a stable salinity reading.
- Important: Do not place the electrode in viscous, organic liquids, such as heavy oils, glycerin (glycerol), or ethylene glycol. Do not place the probe in acetone or non-polar solvents, such as pentane or hexane.
Using the Salinity Sensor with Other Vernier Sensors
Some combinations of sensors interfere with each other when placed in the same solution. The degree of interference depends on many factors, such as the combination of sensors being used and the interface to which the sensors are connected. For more information, see www.vernier.com/til/638
Sampling in the Field
In free-flowing streams, there will usually be good mixing of the water, so that samples taken near the current will be a good representative of the stream as a whole. If you are sampling an impounded stream or a lake, there will be very little mixing. Therefore, it is important to sample away from shore and at different depths, if possible. Do not immerse the Vernier Salinity Sensor above the top of the electrode because the connection between the electrode and the handle is not waterproof. The electrode is not constructed to withstand higher pressures, thus seepage into electronic components of the electrode will result. Although it is better to take readings at the collection site, readings of salinity should not change significantly if you collect samples and take readings at a later time. However, be sure that samples are capped to prevent evaporation.
If sample bottles are filled brim full, then a gas such as carbon dioxide, which is capable of forming ionic species in solution, is prevented from dissolving in the water sample. Since the probe has built-in temperature compensation, you can do your calibration in the lab. This means that even though you will be sampling in water that has a different temperature than your calibration temperature, the probe will take correct readings at the new sampling temperature.
Calibrating the Sensor
For many experiments, calibrating the Salinity Sensor is not required. We store a calibration equation on each sensor before shipping it, which is used as a default by our software.
For the most accurate measurements with this sensor, we recommend calibration. It is a simple process that takes only a few minutes.
- For instructions for Salinity Sensor calibration using Logger Pro computer software, see www.vernier.com/til/2341
- For instructions for Salinity Sensor calibration using LabQuest App, see www.vernier.com/til/3394
- For instructions for Salinity Sensor calibration using Graphical Analysis with a Chromebook, see www.vernier.com/til/3631
- For instructions for Salinity Sensor calibration using Graphical Analysis with an iOS or Android device, see www.vernier.com/til/3630
Making Standard Calibration Solutions
If you choose to calibrate the Salinity Sensor, you will want an accurate standard solution. Vernier sells a 35 ppt standard solution (order code SAL-ST). To prepare your own 35 ppt standard solution using solid NaCl, use a container with accurate volume markings (e.g., volumetric flask). Add 33.03 g NaCl to enough distilled water to make 1 liter of solution. Use reagent grade NaCl.
Note: The Practical Salinity Scale 1978 was developed relative to a KCl solution. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater states that “A seawater with a conductivity at 15°C equal to that of a KCl solution containing a mass of 32.4356 g in a mass of 1 kg of solution is defined as having a practical salinity of 35.”
Automatic Temperature Compensation
Your Vernier Salinity Sensor is automatically temperature compensated between temperatures of 5°C and 35°C. Note that the temperature of a solution is being read by a thermistor that extends into the space between the graphite electrodes. Readings are automatically referenced to a salinity value at 25°C. Therefore, the Salinity Sensor will give the same reading in a solution that is at 15°C as it would if the same solution were warmed to 25°C. This means you can calibrate your probe in the lab, and then use these stored calibrations to take readings in colder (or warmer) water in a lake or stream. If the probe was not temperature compensated, you would notice a change in the reading as temperature changed, even though the actual ion concentration did not change.
Specifications
|
Range of Salinity Sensor |
0 to 50 ppt (0 to 50,000 ppm) |
|
Accuracy using factory calibration |
±3% of full scale (calibrated at 17.5 and 35 ppt) |
|
Accuracy using custom calibration |
±1% of full scale (user calibrated) |
|
Response time |
90% of full-scale reading in 10 s |
|
Temperature compensation |
automatic from 5 to 35° C |
|
Temperature range (can be placed in) |
0 to 80°C |
|
Cell constant |
10 cm-1 |
|
Description |
dip type, epoxy body, parallel platinum electrodes |
|
Dimensions |
12 mm OD and 150 mm length |
|
Calibration values |
slope: 16.3 ppt/V |
Care and Maintenance
When you have finished using the Salinity Sensor, simply rinse it off with distilled water and blot it dry using a paper towel or lab wipe. The probe can then be stored dry.
Do not wrap the cable tightly around the sensor for storage. Repeatedly doing so can irreparably damage the wires and is not covered under warranty.
How the Sensor Works
The Vernier Salinity Sensor measures the ability of a solution to conduct an electric current between two electrodes. In solution, the current flows by ion transport; therefore, an increasing concentration of ions in the solution will result in higher conductivity values.
The Salinity Sensor is actually measuring conductance, defined as the reciprocal of resistance. Even though the Salinity Sensor is measuring conductance, we are interested in finding conductivity of a solution. A potential difference is applied to the two probe electrodes in the Salinity Sensor. The resulting current is proportional to the conductivity of the solution. This current is converted into a voltage.
Alternating current is supplied to prevent the complete ion migration to the two electrodes. As shown in Figure 1, with each cycle of the alternating current, the polarity of the electrodes is reversed, which in turn reverses the direction of ion flow. This very important feature of the Salinity Sensor prevents most electrolysis and polarization from occurring at the electrodes. Thus, the solutions that are being measured for conductivity are not fouled. It also greatly reduces redox products from forming on the electrodes.

Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting and FAQs, see www.vernier.com/til/1382
Repair Information
If you have followed the troubleshooting steps and are still having trouble with your Salinity Sensor, contact Vernier Technical Support at support@vernier.com or call 888-837-6437. Support specialists will work with you to determine if the unit needs to be sent in for repair. At that time, a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number will be issued and instructions will be communicated on how to return the unit for repair.
Warranty
Warranty information for this product can be found on the Support tab at www.vernier.com/sal-bta/#support
General warranty information can be found at www.vernier.com/warranty
Disposal
When disposing of this electronic product, do not treat it as household waste. Its disposal is subject to regulations that vary by country and region. This item should be given to an applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic equipment. By ensuring that this product is disposed of correctly, you help prevent potential negative consequences on human health or on the environment. The recycling of materials will help to conserve natural resources. For more detailed information about recycling this product, contact your local city office or your disposal service.
Battery recycling information is available at www.call2recycle.org
Do not puncture or expose the battery to excessive heat or flame.
 The symbol, shown here, indicates that this product must not be disposed of in a standard waste container.
The symbol, shown here, indicates that this product must not be disposed of in a standard waste container.
Contact Support
Fill out our online support form or call us toll-free at 1-888-837-6437.

